Why Do Cats Bite Each Other’s Necks? Cat Behavior Explained!
Have you ever wondered why cats bite each other’s necks? This common behavior observed in feline social interactions can sometimes raise concerns among pet owners. Understanding the reasons behind this behavior is crucial in ensuring a harmonious and safe environment for our furry friends.
In this article, we will explore the various factors that contribute to cats biting each other’s necks. From cat social hierarchies and dominance to play behaviors and courtship rituals, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of cat behavior and shed light on why cats exhibit this unique behavior.
Whether you’re a male cat owner or simply curious about feline behavior, this article will provide valuable insights into the motivations behind cat neck biting and offer tips for managing and preventing two cats aggression.
Key Takeaways:
- Cats biting each other’s necks is a common behavior and natural instinct observed in feline communication.
- Understanding cat social hierarchies and dominance is crucial in comprehending why cats engage in neck biting.
- Rough play biting and aggressive biting are two different behaviors, and it’s important to differentiate between them.
- Cats may express neck biting during mating rituals as part of cats’ reproductive instincts.
- Creating a cat-friendly environment and seeking professional help when needed can help manage and reduce cat-biting behaviors.
Understanding Cat Social Hierarchies and Dominance
Cats are known for their independent and solitary nature, but in multi-cat households, they establish social hierarchies. Within these hierarchies, dominant cats display certain behaviors that establish their authority. Understanding cat dominance and recognizing the signs of dominance in feline behavior can help you comprehend why male cats bite each other’s necks.
Defining Cat Dominance
Cat dominance refers to the social hierarchy established among cats living together. Dominant cats display behaviors like resource guarding, posturing, and asserting themselves over other cats. By understanding these behaviors, we can decode the reasons for neck biting in cats, giving us insight into their social dynamics.
Signs of Dominance in Feline Behavior
Even domestic cats exhibit various signs of dominance, indicating their social hierarchy position. These signs can include aggression towards other cats, claiming resources, and displaying confident body language. Identifying dominant cat signs is essential in understanding the motivations behind neck-biting and deciphering the complex social dynamics among cats’ behavior.
Role of Neck Biting in Cat Hierarchies
Neck biting is a common behavior observed in cats during social interactions. It can serve as a way for dominant cats to establish and maintain their position in the social hierarchy. Neck biting can be a display of dominance and communication between cats.
Understanding cat social hierarchies and dominance is essential for creating a harmonious environment for our feline companions. By recognizing the signs of dominance and the role of the normal behavior of neck biting, we can better manage and prevent aggressive behaviors among cats, ensuring a peaceful coexistence.
Male Cat Biting Other Cats’ Neck: Normal or Aggressive Behavior?
Cats biting each other’s necks can be a cause for concern for pet owners. Distinguishing between normal play behavior and aggressive behavior is essential in addressing the issue effectively. This section explores the differences between playful biting and aggressive biting and highlights the role of social learning through play in kittens.
Seeing your cat bite the other cats necks is likely them exerting dominance over one cat. Even fixed male cats may display a mating behavior over female cats or young cats.
Playful Biting vs. Aggressive Biting: How to Tell the Difference
Playful biting is a natural behavior for cats, especially if they are playing with the other cat. Cats engage in mild biting as a way to establish boundaries and engage in social interaction. The cat’s body language is less aggressive and more relaxed in play biting.
Aggressive biting is often accompanied by hissing, growling, raised fur, and a tense body posture, indicating a threat or an imminent prey attack.
However, aggressive biting can be a sign of certain medical conditions or underlying issues such as fear, anxiety, or territoriality. There could even be medical reasons, hormonal imbalances, or medical conditions that should be addressed with your vet.
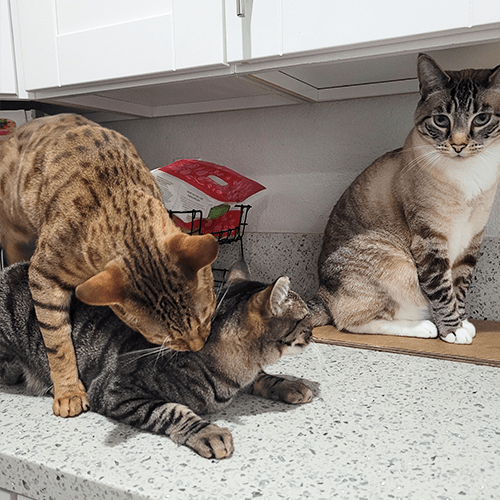
Social Learning Through Play in Kittens
Kittens learn important social skills through play, including appropriate bite inhibition. During play sessions, kittens engage in gentle biting to explore their environment, hone their hunting skills, and establish boundaries with their littermates. Through play, kittens learn how much force to exert during biting and develop communication and social boundaries.
Playful bites are a vital part of animal development and help pets acquire the skills necessary for adult social interactions. However, intervention and training may be necessary if these behaviors persist into adulthood or become aggressive.
Mating Behavior: Neck Biting as a Courtship Activity
Neck biting can also be observed during mating behaviors, often seen in unfixed outdoor neighborhood cats. It is a common and natural cat behavior that plays a significant role in cat courtship. During the mating ritual, male cats often engage in neck biting as part of their reproductive instincts.
This behavior serves multiple purposes. First, it allows the male cat to establish physical contact with the female cat, indicating his interest and intentions. Additionally, neck biting stimulates the female cat and enhances her receptivity to mating.
Understanding these mating behaviors provides valuable insights into the natural tendencies of cats during the reproductive process. It helps us comprehend just what the intricacies of feline courtship and the roles that different behaviors, such as neck biting, play in this process.
When Cat Play Escalates to Aggression
Play is a natural part of feline behavior and an important way for cats to learn and socialize. However, sometimes play can escalate to aggression, leading to biting and other aggressive behaviors. Understanding the reasons behind this escalation is key to managing and redirecting these behaviors effectively.
There are several factors that can contribute to play turning into aggression in cats. One common cause is overstimulation during play. When cats become overly excited or aroused, their play behavior can become more intense and may escalate to aggression. Additionally, certain triggers, such as sudden movements or loud noises, can also lead to aggressive responses during play.
It’s important to recognize the signs that play is turning into aggression. These may include aggressive body language, such as flattened ears, dilated pupils, hissing, growling, or a stiff body posture. If you notice these signs, it’s crucial to intervene to prevent the situation from escalating further.
To manage and redirect play aggression in cats, there are several strategies you can try. Providing appropriate outlets for play, such as interactive toys or play sessions with you, can help redirect their energy in a positive way. Additionally, offering environmental enrichment, such as scratching posts or puzzle toys, can help satisfy their natural instincts and prevent boredom-related aggression.
It’s also important to set boundaries during play and establish clear rules. If your cat becomes overly stimulated during play, immediately stop the play session and redirect their attention to an appropriate toy or activity. Consistency and positive reinforcement can help reinforce these boundaries over time.
If your cat’s aggressive behavior during play persists or worsens, it’s recommended to consult with a veterinarian or animal behaviorist for further guidance. They can provide a professional assessment of the situation and offer tailored advice about redirected aggression or behavioral therapy to address the underlying causes of aggression.
Signs of Cat Territorial Aggression
Cat territorial aggression is a common cause of cats biting each other’s necks. Cats have a strong instinct to protect their territory, and aggression can arise when their space feels threatened. Understanding the signs of cat territorial aggression is crucial in managing and preventing conflicts among cats.
Marking Territory and Cat Aggression
Cats use scent marking as a way to claim their territory and communicate with other cats. This can involve rubbing their scent glands on furniture, scratching, and urine marking. When another cat invades their marked territory, it can trigger territorial aggression, leading to neck biting and other aggressive behaviors.
Scent marking is an important aspect of cat territorial behavior and serves as a way for cats to establish boundaries and communicate their presence to other cats.
How Cats Establish and Maintain Territories
Cats establish their territories through a combination of scent marking, body language, and other behaviors. By marking their territory with their scent, cats communicate to other cats that the area is claimed and should be respected. Maintaining their territory involves defending it when necessary, which may manifest as aggression towards other cats.
By respecting a cat’s need for space and providing appropriate resources and environmental enrichment, pet owners can help minimize territorial aggression and promote a harmonious coexistence among cats.
Managing Multi-Cat Households to Prevent Neck Biting
Multi-cat households require careful management to avoid conflicts and prevent cats from biting each other’s necks. Creating a harmonious environment for multiple cats is crucial in reducing the likelihood of aggressive behaviors. Here are some practical tips and strategies to help you manage your multi-cat household:
- Provide Sufficient Resources: Ensure that each cat has access to their own food and water bowls, litter boxes, scratching posts, and resting areas. Having enough resources can help reduce competition and territorial disputes.
- Separate Feeding Areas: Cats may become territorial during mealtimes. To prevent food-related conflicts, feed your cats in separate areas or use individual feeding stations to minimize interaction.
- Create Vertical Space: Cats appreciate vertical territory, as it allows them to observe their surroundings and establish personal space. Provide vertical elements such as cat trees, shelves, or perches to give each cat their own vantage point and escape route.
- Introduce New Cats Gradually: When introducing a new cat to your existing feline companions, do so slowly and in a controlled manner. Use scent-swapping techniques, separate living spaces, and gradual supervised interactions to help the cats become acquainted without triggering aggression.
- Manage Stress: Cats can become stressed in multi-cat households, which may escalate into aggression. Minimize environmental stressors by providing hiding spots, using pheromone diffusers, and maintaining a consistent routine.
- Facilitate Play and Exercise: Encourage interactive play sessions among your cats by using toys and engaging them in games. Play helps cats release excess energy and establish positive social connections.
- Neutering/Spaying: Having your cats neutered or spayed can help reduce territorial behaviors and aggression related to mating instincts.
How to Stop Cats from Fighting and Biting
This section provides strategies for addressing and de-escalating cat fights, making appropriate environmental adjustments to reduce conflict, and approaching behavioral modification to resolve aggression issues.
Intervening in Cat Fights
When animals engage in aggressive behaviors and fights, it is crucial for pet owners to intervene safely and effectively. To break up a cat fight without causing harm to yourself or the cats involved, consider the following tips:
Safely Breaking Up Cat Fights:
- Use a loud noise, such as clapping your hands or shaking a can filled with coins, to startle the cats and interrupt the fight.
- Avoid physically intervening with your hands or body, as this can result in injury. Instead, use a broom or a large object to create a barrier between the fighting cats.
- If the cats are wearing collars, firmly grasp the scruff of the neck (the loose skin at the back of the neck) and gently pull them apart.
- If the fight continues or escalates, consider using a water spray bottle to deter aggression.
Environmental Adjustments to Reduce Conflict
Creating a cat-friendly environment can significantly reduce conflicts and decrease the likelihood of cats biting each other’s necks. Consider the following environmental adjustments:
Creating a Harmony-Inducing Environment for Cats:
- Ensure that each cat has its own designated space, such as a separate room or a designated area within a room, where they can retreat and feel safe.
- Provide multiple litter boxes in different locations throughout the house to prevent resource guarding and territorial disputes.
- Offer plenty of vertical spaces, such as cat trees or high shelves, where cats can perch and observe their surroundings from a safe vantage point.
- Utilize pheromone diffusers, such as Feliway, which release calming pheromones that can help reduce stress and promote a sense of security among cats.
Reducing Cat Conflict Through Environmental Enrichment:
- Provide a variety of interactive toys, scratching posts, and puzzle feeders to keep your cats mentally and physically stimulated, reducing the likelihood of boredom-driven aggression.
- Rotate and introduce new toys regularly to maintain your cats’ interest and prevent possessiveness over specific toys.
- Ensure that each cat has access to their preferred resting spots and sleeping areas to minimize competition and potential conflicts.
- Offer frequent grooming, nail trimming, and overall good cat care to keep your kitty feeling their best.
Approaching Behavioral Modification
Behavioral modification techniques can help address and mitigate cat aggression, including biting behaviors. Consider the following approaches:
Behavior Modification Techniques for Aggressive Cats:
- Implement positive reinforcement training to encourage desired behaviors and reward your cats for calm and non-aggressive interactions.
- Use desensitization techniques, gradually exposing your cats to triggers that may elicit aggressive reactions while rewarding them for remaining calm and non-reactive.
- Consider consulting with a professional animal behaviorist who can provide tailored guidance and develop a behavior modification plan specific to your cats’ needs.
Positive Reinforcement Training for Aggression in Cats:
- Use treats, praise, or play as rewards when your cats display appropriate social behaviors and refrain from aggression.
- Redirect aggressive behaviors by providing alternative outlets for their energy, such as interactive toys or engaging in structured play sessions.
- Consistency and patience are key when implementing behavioral modification techniques. It may take time for your cats to adapt and change their behavior patterns.
Professional Help: When to Consult a Veterinarian or Behaviorist
While understanding and addressing cat aggression and biting behaviors can often be accomplished through various techniques and strategies, there are cases where seeking professional help becomes necessary. Consulting with a veterinarian or animal behaviorist can provide invaluable guidance and expertise in managing these challenging behaviors. It is important to recognize the situations in which professional intervention is recommended and to explore the different approaches available.
Distinguishing Between Play, Aggression, and Medical Issues
When encountering cat aggression and biting behaviors, it is crucial to differentiate between different underlying causes. Professional help can assist in assessing whether the behavior is linked to play, territoriality, fear, stress, or potential medical issues.
Veterinarians and behaviorists can conduct a comprehensive evaluation to accurately identify the root causes and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Behavioral Therapy for Cats
Behavioral therapy offers a structured approach to modifying cat behavior problems and reducing aggression. Behaviorists can help cats develop new coping mechanisms, modify their responses, and create positive behavioral changes by employing techniques such as positive reinforcement, desensitization, and counter-conditioning.
A customized treatment plan can be designed to address specific concerns and improve the overall well-being of the cat.
In summary, consulting a veterinarian or behaviorist can provide valuable insights into cat aggression and biting behaviors. These professionals can help distinguish between play, aggression, and medical issues, as well as provide effective behavioral therapy to address these problems. Seeking professional help is an important step towards promoting a safe and harmonious environment for both cats and their owners.
Conclusion
Cat biting behaviors, such as neck biting, can stem from various factors, including dominance, play, courtship, and aggression. Understanding the underlying causes behind these behaviors is essential for cat owners to effectively manage and create a harmonious environment for their feline companions.
By implementing proper management strategies, such as establishing clear social hierarchies, providing enriching play opportunities, and creating a cat-friendly territory, pet owners can significantly reduce instances of cat biting. Additionally, if the behavior persists or escalates, seeking professional help from a veterinarian or animal behaviorist is recommended.
Remember, addressing cat-biting problems requires patience, consistency, and understanding. With the right approach and proper care, cat owners can successfully reduce cat biting behaviors, leading to a happier and healthier cat household.
About the Author: Justin Ruffier
My journey with TNR began in the canyon behind my house. A few kittens were playing in the dandelions, and I began to name them. Then, one day, they showed up with ear tips. I wasn’t sure what to think, so I began researching. I learned that TNR was about helping community cats, and I began to find ways to help others in my community. I’m a cat advocate, marketer, and fundraising specialist, and I want to help all outdoor cats find safe indoor homes or have safe outdoor communities.




